Skin changes can be alarming, especially when they appear suddenly or cause intense itching. If you're a woman struggling with unexplained skin flare-ups, you might be wondering about the difference between hives and rashes. Are they the same thing? Could your diet be playing a role?

This article delves into the world of skin reactions, exploring the distinctions between hives and rashes, their potential causes, and how food intolerances might be contributing to your discomfort.
Hives vs. Rash: Understanding the Basics
While the terms "hives" and "rash" are often used interchangeably, they have distinct characteristics:
-
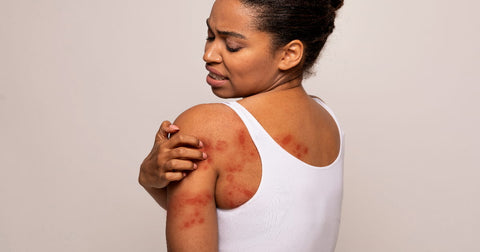
Hives: Also known as urticaria, hives are raised, itchy welts that appear on the skin. They are often triggered by an allergic reaction and can vary in size and shape.
-
Rash: A broader term for any skin irritation or inflammation that causes a change in color, texture, or appearance. Rashes can be caused by various factors, including allergies, infections, and underlying medical conditions.
Are Hives Contagious?
No, hives themselves are not contagious. They are an allergic reaction specific to the individual and cannot be spread from person to person. However, the underlying cause of the hives, such as a viral infection, might be contagious.
Can Food Cause Hives?

Yes, food allergies are a common trigger for hives. When your body encounters an allergen, it releases histamine and other chemicals that cause the skin to react with raised, itchy welts.
Common food allergens that can cause hives include:
-
Shellfish
-
Peanuts and tree nuts
-
Milk and dairy products
-
Eggs
-
Soy
-
Wheat
Food Intolerance and Hives: The Connection
While food allergies trigger an immediate immune response, food intolerances involve a different mechanism. Your body might struggle to digest certain foods, leading to a delayed reaction that can include hives, digestive upset, or other symptoms.
Food Sensitivity Test Kit: Identifying Your Triggers
If you suspect a food intolerance is contributing to your hives or other symptoms, a food sensitivity test kit can help identify specific trigger foods. By eliminating or reducing these foods from your diet, you can potentially alleviate your symptoms and improve your overall health.
Hives vs. Rash: Distinguishing Features
While hives are a type of rash, they have distinct characteristics:

-
Appearance: Hives are raised, itchy welts, while rashes can have various appearances, including redness, bumps, blisters, or scaling.
-
Duration: Hives typically appear suddenly and disappear within 24 hours, while other rashes can last for days, weeks, or even longer.
-
Cause: Hives are often caused by allergic reactions, while rashes can have various causes, including infections, irritants, and underlying medical conditions.
Elimination Diet: Identifying Food Triggers
An elimination diet involves removing suspected trigger foods from your diet for a period and then gradually reintroducing them to see if they cause symptoms. This can be a helpful tool for identifying food intolerances that might be contributing to your hives or other health issues.
Key Takeaways:
-
Hives are a type of rash characterized by raised, itchy welts, often caused by allergic reactions.
-
Food allergies and intolerances can both trigger hives.
-
A food sensitivity test can help identify specific food triggers.
-
If you have a rash that won't go away, consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.

Remember, this article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have any concerns about your health or are experiencing hives or a rash, consult a qualified healthcare professional.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Are hives always caused by allergies?
While allergies are a common trigger, hives can also be caused by other factors, such as medications, insect bites, infections, or even stress. If you're unsure about the cause of your hives, consult a doctor.
2. How can I tell the difference between hives and other types of rashes?
Hives are typically raised, itchy welts that appear and disappear relatively quickly, often within 24 hours. Other rashes might have different appearances, such as redness, bumps, or scaling, and can last for longer periods. If you're unsure about a rash, it's best to see a doctor for diagnosis.
3. Can I treat hives at home?
For mild hives, over-the-counter antihistamines and cool compresses can help relieve itching and swelling. However, if your hives are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms like difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately.
4. What is involved in a food sensitivity test?
A food sensitivity test typically involves a blood sample or a skin prick test to assess your body's reaction to various foods. It can help identify potential triggers for hives or other symptoms like digestive upset or skin problems.
5. I've tried avoiding common allergens, but I still get hives. What else can I do?
Consider keeping a food diary to track your meals and any associated symptoms. This can help identify potential triggers. You might also consult a doctor or allergist for further evaluation and guidance. An elimination diet can also be helpful in pinpointing specific food sensitivities.

.png?v=1737390083)
.png?v=1737187409)


