Probiotics, known for their role in promoting a healthy gut, have become a staple in the dietary supplements aisle of health food stores and a topic of interest among health enthusiasts. Amidst the wide variety of probiotic products, a particular category, known as "green probiotics," has garnered attention for its unique source and natural benefits. Green probiotics, distinct for being derived from plant-based sources, offer a natural and holistic approach to enhancing gut health and, by extension, the immune system.

The concept of using beneficial bacteria to improve health is not new; however, the understanding and appreciation of the specific advantages provided by green probiotics are still emerging. Unlike their dairy-based counterparts, green probiotics originate from fermented plant foods, making them an excellent option for vegans, vegetarians, and those with dairy sensitivities. But their appeal does not stop there; green probiotics also bring a diverse array of microbial life to the gut—a key factor in maintaining a balanced and resilient microbiome.
The purpose of this article is to delve into the world of green probiotics and uncover how they can bolster the immune system. By exploring the connection between the gut microbiome and immune health, the benefits of incorporating green probiotics into one's diet, and practical tips for doing so, this article aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of how green probiotics can support their overall well-being.
Understanding Probiotics
Probiotics are often heralded as the guardians of gut health, a concept that has captivated the attention of health enthusiasts and medical professionals alike. But what exactly are probiotics? At their core, probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host. They are commonly known as "good" or "friendly" bacteria because they help keep the gut healthy.
Probiotics come from various sources, including dairy products like yogurt and kefir, as well as fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha. These traditional sources are rich in a variety of probiotic strains. However, an exciting and emerging category known as "green probiotics" focuses on plant-based sources, offering a natural and often vegan-friendly alternative.
The distinction between traditional probiotics and green probiotics primarily lies in their origin. While traditional probiotics are often derived from dairy or fermented foods, green probiotics come from fermenting plant materials, such as fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes. This not only makes them suitable for those following a vegan or plant-based diet but also introduces a different spectrum of bacterial strains that may have unique health benefits.
The importance of biodiversity in probiotic strains cannot be overstated. Just as a diverse ecosystem is more resilient and capable of thriving under various conditions, a diverse gut microbiome is better equipped to maintain health and fight off disease. Different strains of probiotics offer different benefits, including supporting gut barrier integrity, modulating the immune system, and even influencing mood and mental health through the gut-brain axis.
The Immune System and Gut Health Connection
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and toxins. Its primary goal is to identify and eliminate pathogens while maintaining a delicate balance to prevent harmful overreactions, such as autoimmune diseases.
One of the key players in this intricate defense system is the gut microbiome, the vast community of microorganisms that resides in our gastrointestinal tract. Comprising trillions of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microbes, the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, including immune function.
Research over the past few decades has revealed a strong connection between gut health and the immune system, often referred to as the gut-immune axis. This bidirectional communication pathway involves complex interactions between gut microbes, immune cells, and various signaling molecules. Here's how it works:
- Modulation of Immune Response: The gut microbiome helps educate the immune system, teaching it to distinguish between harmless substances and potentially harmful pathogens. Certain gut bacteria produce metabolites and signaling molecules that regulate immune cell activity, promoting a balanced and appropriate immune response.
- Barrier Function: The gut lining serves as a barrier that prevents harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. A healthy gut microbiome helps maintain the integrity of this barrier by producing substances that strengthen the gut lining and regulate its permeability. This barrier function is essential for preventing the systemic spread of pathogens and reducing the risk of immune activation and inflammation.
- Production of Immunomodulatory Molecules: Gut microbes produce a variety of compounds, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), that have immunomodulatory effects. SCFAs, in particular, play a crucial role in regulating immune cell function and inflammation within the gut and beyond. By influencing immune cell behavior, these molecules help maintain immune homeostasis and reduce the risk of inflammatory disorders.
- Regulation of Systemic Inflammation: Imbalances in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, have been linked to increased systemic inflammation, which can contribute to a wide range of health problems, including autoimmune diseases, allergies, and metabolic disorders. By promoting a diverse and balanced gut microbiome, people may be able to mitigate inflammation and support overall immune health.
Benefits of Green Probiotics
In recent years, the spotlight on probiotics has intensified as researchers delve deeper into understanding the intricate relationship between gut health and overall well-being. Among the myriad probiotic options available, green probiotics stand out for their unique composition and potential benefits, particularly in bolstering the immune system.
Enhanced Production of Natural Antibodies:
One of the key ways green probiotics contribute to immune health is by promoting the production of natural antibodies within the body. These antibodies play a crucial role in defending against harmful pathogens, viruses, and bacteria that we encounter daily. By stimulating the immune system's antibody response, green probiotics help fortify our defenses, reducing the likelihood of infections and illnesses.
Increased Resistance to Harmful Pathogens:
Green probiotics, derived from plant-based sources, contain a diverse array of beneficial microorganisms that can help create a hostile environment for harmful pathogens. By colonizing the gut and competing with potentially harmful bacteria for resources and space, green probiotics can effectively inhibit the growth of pathogens, thereby reducing the risk of gastrointestinal infections and other immune-related disorders.
Improved Digestion and Nutrient Absorption:

While not a direct immune-boosting mechanism, the role of green probiotics in promoting optimal digestion and nutrient absorption indirectly supports immune health. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for efficient nutrient uptake, ensuring that the body receives the vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants necessary for immune function. By maintaining a balanced microbial ecosystem in the gut, green probiotics contribute to overall digestive wellness, which in turn supports a robust immune response.
Sources of Green Probiotics
Green probiotics, derived from plant-based sources, offer a rich array of beneficial microorganisms that can support a healthy gut microbiome and, consequently, enhance your immune system. Incorporating these sources into your diet can be a delicious and nutritious way to promote overall wellness. Here's a closer look at some of the top sources of green probiotics:
- Fermented Vegetables: Fermented vegetables are excellent sources of green probiotics. Foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and pickles are not only tasty additions to meals but also brimming with beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. These bacteria help diversify your gut microbiota, strengthening your immune defenses.
- Kombucha: Kombucha, a fermented tea beverage, has gained popularity for its tangy taste and purported health benefits. Made from sweetened tea that undergoes fermentation with the help of a SCOBY (symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast), kombucha is rich in probiotics, including species like Saccharomyces boulardii and various lactobacilli. Incorporating kombucha into your routine can introduce these beneficial microbes to your gut ecosystem.
- Tempeh: Tempeh, a traditional Indonesian food made from fermented soybeans, is not only a great source of plant-based protein but also contains probiotic bacteria, primarily strains of Bacillus subtilis. This fermented soy product offers a savory flavor and a chewy texture, making it a versatile ingredient for various dishes.
- Miso: Miso, a staple in Japanese cuisine, is a fermented paste typically made from soybeans, rice, or barley. It contains probiotic strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which develop during the fermentation process. Miso adds depth of flavor to soups, dressings, and marinades while providing gut-friendly bacteria.
- Fermented Soy Products: Beyond tempeh and miso, other fermented soy products like natto can also contribute to your probiotic intake. Natto, a traditional Japanese dish made from fermented soybeans, contains a potent probiotic strain called Bacillus subtilis var. natto, known for its potential health benefits, including immune support.
Incorporating Green Probiotics into Your Lifestyle

Incorporating green probiotics into your lifestyle doesn't have to be a daunting task. With a few simple adjustments to your diet and habits, you can reap the benefits of these natural immune boosters. Here's how to get started:
- Prioritize Plant-Based Fermented Foods: Start by incorporating more plant-based fermented foods into your diet. These include classics like sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso, as well as lesser-known options like fermented vegetables, tempeh, and kombucha. These foods are rich in a variety of probiotic strains that can help diversify your gut microbiome and support immune function.
- Experiment with Homemade Ferments: Get creative in your kitchen by trying your hand at making homemade ferments. Making your own fermented foods not only ensures freshness but also allows you to control the ingredients and fermentation process. Consider experimenting with homemade pickles, fermented hot sauces, or even cultured nut cheeses. There are plenty of resources online to guide you through the fermentation process, making it a fun and rewarding culinary adventure.
- Embrace Leafy Greens and Cruciferous Vegetables: In addition to fermented foods, incorporate plenty of leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables into your meals. These plant-based foods are not only rich in essential nutrients but also contain prebiotic fibers that feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Aim to include a variety of greens such as spinach, kale, collard greens, and broccoli in your daily meals to support a thriving gut microbiome.
- Consider Probiotic Supplements: If you find it challenging to consume enough probiotic-rich foods on a daily basis, consider incorporating a high-quality probiotic supplement into your routine. Look for supplements that contain a diverse range of bacterial strains, including those derived from plant sources. Start with a lower dosage and gradually increase as needed, paying attention to how your body responds.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are green probiotics, and how are they different from traditional probiotics?
Green probiotics are probiotic strains sourced from plant-based sources, such as fermented vegetables, fruits, and grains. They differ from traditional probiotics, which are typically derived from dairy or other animal products. Green probiotics offer a vegan-friendly option for those seeking to support gut health and immunity without relying on animal-derived products.
How do green probiotics enhance the immune system?
Green probiotics support immune function by promoting a healthy balance of gut bacteria. They help regulate the immune response, stimulate the production of natural antibodies, and enhance the gut barrier function, thereby reducing the risk of infections and inflammation. By fostering a diverse and robust gut microbiome, green probiotics contribute to overall immune resilience.
Can I get enough green probiotics from my diet alone, or do I need supplements?
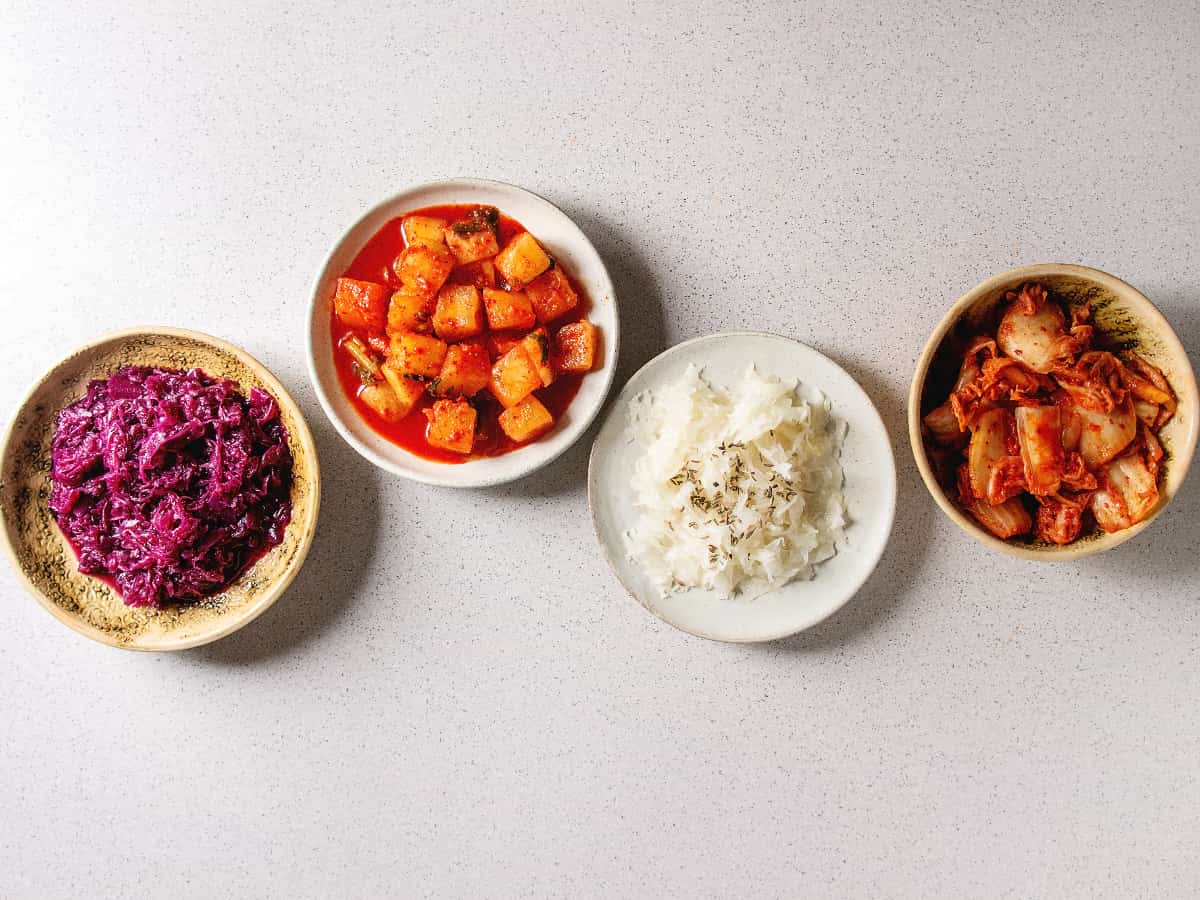

While incorporating fermented plant foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and tempeh into your diet can provide beneficial green probiotics, supplementation may be necessary for some people. Factors such as dietary preferences, digestive health, and lifestyle may influence the need for supplementation.
Are there any side effects associated with consuming green probiotics?
In general, consuming green probiotics from natural sources is safe for most people and rarely causes adverse effects. However, some people may experience mild digestive discomfort, such as bloating or gas, especially when first introducing probiotic-rich foods into their diet. These symptoms typically subside as the gut microbiome adjusts.
How long does it take to experience the benefits of green probiotics on immune health?
The timeline for experiencing the benefits of green probiotics on immune health can vary depending on individual factors such as diet, lifestyle, gut health, and the specific strains consumed. While some people may notice improvements in digestion and overall well-being within a few weeks of regular consumption, it may take longer to observe significant changes in immune function.
Conclusion
In the pursuit of optimal health and well-being, the importance of a thriving immune system cannot be overstated. Throughout this exploration of green probiotics and their potential to enhance immune function, it becomes increasingly clear that nurturing the gut microbiome is key to supporting our body's defense mechanisms.
From understanding the intricate relationship between gut health and the immune system to delving into the specific benefits of green probiotics, we've uncovered a wealth of knowledge that underscores the significance of incorporating these beneficial microorganisms into our daily routines.
By embracing natural sources of green probiotics, such as fermented plant foods, and considering high-quality supplements when necessary, we have the opportunity to fortify our immune defenses from within. However, it's important to remember that achieving a balanced and diverse gut microbiome is a journey rather than a destination. Consistency, variety, and mindful consumption are the cornerstones of success in this endeavor.
As we conclude our discussion, let us reaffirm our commitment to prioritizing our gut health and, by extension, our immune resilience. Let us embrace the power of green probiotics as a gentle yet potent ally in our quest for vitality and longevity. Together, let's embark on this journey towards holistic well-being, fortified by the wonders of nature's green microbiome.


.png?v=1737390083)
.png?v=1737187409)


